Two Ideas for a Digital Future
Blockchains can be applied to thousands of industries. Believers in the new blockchain-powered smart economy believe that financial, logistical and energy industries will be revolutionised by implementing the blockchain.
For example, smart contracts and decentralized networks could make energy a publicly owned service, remove trust from messaging applications and provide the foundation for a new era in cloud computing.
This is what NEO and Ethereum are all about. Providing the best blockchain platform for the whole world to build decentralized blockchain projects on.
The result of these ambitions is a growing industry with competitors of early IBM, Apple and Microsoft proportions. One ingenious developer, marketing campaign or industry sponsor could secure the battle between Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, NEO, Cardano, EOS, Lisk and hundreds of other projects.
Introducing NEO
NEO is backed by a Chinese company called OnChain. Despite only recently seeing a surge in popularity, the platform has been around since 2014. Founded by blockchain entrepreneurs Da Hongfei and Erik Zhang, it was the first open source blockchain project in China, hence it’s nickname “China’s Ethereum”.

Branded as ‘Antshares’ until a rebranding in mid 2017, NEO’s misison is to build a smart economy. By enabling digital assets, digital identities and a system of smart contracts, NEO plans to become the blockchain powerhouse, starting with the Eastern markets.
The NEO project has a secondary token, GAS, used to pay out rewards for participation in their cryptographic consensus protocol.
Introducing Ethereum
Ethereum, launched in 2015, similarly aims to be an entrepreneurial hub for blockchain projects.
These projects can take advantage of Ethereum blockchain and smart contracts, with management help from Ethereum crowdsale and decentralized project management services.

It’s founded by blockchain industry leader Vitalik Buterin, who provides his thoughts on new blockchain technologies in his regular Medium posts.
Ethereum is the industry leader for blockchain services and is backed by a a range of investors, including Fortune 500 companies.
Officially, Ethereum is now run by a Swiss nonprofit called the Ethereum Foundation.
Key Differences
| Ethereum | NEO | |
| Mission | Become a home for decentralized applications | Create a smart economy |
| Inflation | Under 15% p.a., reducing with time | Under 23% p.a. |
| Industry adoption | Very high | Limited, but popular in China |
| Currency governance | Decentralized | Centralized, but decreasingly so |
| Funding | Extremely large | Large |
| Protocol | PoW, moving to PoS | DBFT, no transaction fees |
| Transaction bandwidth | Little | Lots |
| Scalability | Raiden project | Trinity project |
| Future focus |
Blockchain performance and entrepreneurial support | Industry adoption |
Investment Details
Inflation Rates
Most fiat currencies in the world suffer from monetary inflation due to Governments printing money and adding it to the circulating supply. An increase in the supply of currency results in slightly less spending power for everyone, known as price inflation.
Although most cryptocurrencies have a limit to their supply, neither Ethereum or NEO have released the entirety of it into the ecosystems, so their they are still inflationary.
Ethereum
Ethereum’s current proof of work protocol provides a reward in Ethereum tokens to miners who help to validate transactions by solving complex mathematical problems.
The current issuance rate of Ethereum is a set volume per year. However, this means that the inflation rate decreases over time because the pool of funds also grows.
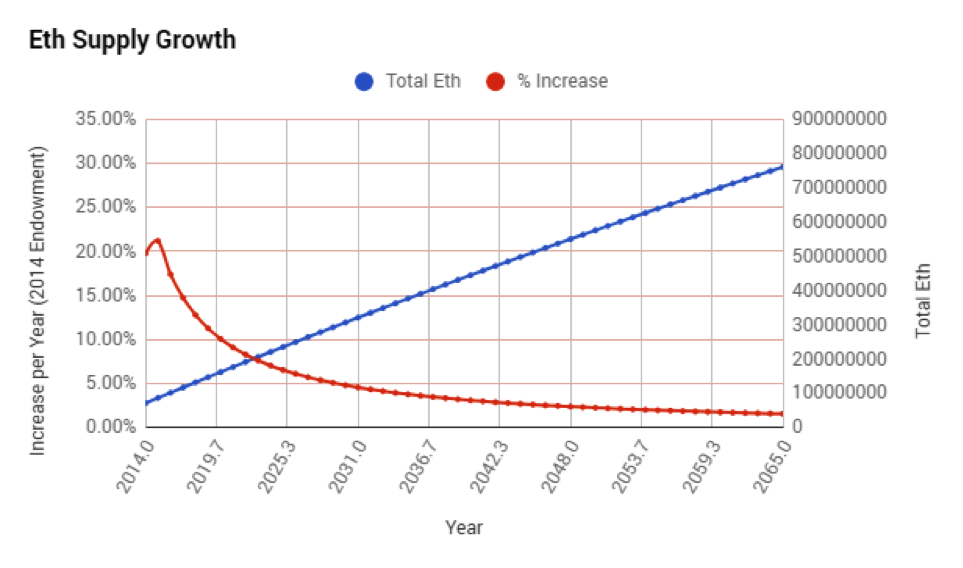
Ethereum total supply (blue) and inflation rate (red). Data source.
The inflation rate slowly decreases over time before it reaches close to zero, but the amount of Ethereum in supply each year still increases linearly.
Ethereum plans to make the switch to the Proof of Work protocol. According to founder Vitalik Buterin, will result in zero to tiny issuance rates and no inflation.
NEO
NEO’s protocol results in block rewards that need to be equally distributed among NEO holders. Owners are rewarded with GAS tokens instead of NEO, so NEO’s price does not inflate due to their protocol. Moreover, every holder of NEO is entitled to regular GAS payouts for holding the coins.
NEO was initially created with a supply cap of 100 million tokens, but only 50 million were put into supply. The rest are in a holding account, which can be monitored by anyone and is slowly drawn from. This is the source of NEO’s inflation.
Their spending plan is available in the NEO whitepaper:
- 10 million tokens (10% total) will be used to motivate NEO developers and members of the NEO Council
- 10 million tokens (10% total) will be used to motivate developers in the NEO ecosystem
- 15 million tokens (15% total) will be used to cross-invest in other block-chain projects, which are owned by the NEO Council and are used only for NEO projects
- 15 million (15% total) will be retained as contingency
- The annual use of NEO in principle shall not exceed 15 million tokens
Thanks to the withdrawal hard cap of 15 million token annually, inflation cannot not exceed 23%.
Withdrawals are taken out slowly. With the intrinsic volatility of NEO’s price, withdrawals are hard to notice in the market.
Despite the high inflation, withdrawals result in value added to the NEO project, so inflation alone is not a reason to avoid investing.
Industry Adoption
Ethereum
Ethereum is undoubtedly the leader of industry applications of the blockchain.
In early 2017 they launched the non-profit Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA), pulling together an impressive range of companies interested in the potential of blockchain technologies into one group. It gives Ethereum a link to crucial industry leaders in the financial sector such as J.P Morgan, ING and UBS, as well as payment processors including MasterCard and tech research giants Microsoft, Intel and the Toyota Research Group.
One of the EEA’s core missions is to provide “resources for businesses to learn about Ethereum and leverage this groundbreaking technology to address specific industry use cases”. Their board comprises of industry founders, managers and researchers all keen to make developments with decentralized applications (dApps).
Ethereum has already been the backbone of over a thousand dApps, and have their doors open for more. Some have already hit the market, but most are startups. Ethlance is a decentralized hub for freelance work, Leeroy is a decentralized Twitter clone and DNN is a network for media moderated by only its readers.
NEO
Although NEO is a smaller project and doesn’t have quite as many partners, they’ve been working with Asian regtech venture company QRC and have supported cryptocurrencies such as Red Pulse, NEX and THEKEY.
They also held an important $490,000 decentralized application competition in collaboration with Microsoft China to spur blockchain development.

The competition saw over 500 submissions, all using the NEO blockchain. The winners included a game based on smart contracts, decentralized marketplaces, and an industry application to thermo-logistics.
NEO’s key for-profit partner, OnChain (also founded by Hongfei and Zhang), plans to work closely with the Chinese Government to bring NEO into every industry niche which could benefit from blockchain technologies.
At a NEO event, cofounder Da Hongfei compared NEO’s philosophy with Ethereum’s. “We want to be more compliant ready”, he said, reiterating the project’s emphasis on achieving industry adoption through the careful consideration of potential regulatory requirements. “It’s time for the blockchain to be connected to the real economy, not just experimental things”.
Currency Governance and Teams
Ethereum
The Ethereum Foundation, the organisation behind the Ethereum project, is still led by original founder Vitalik Buterin.
There are over 40 full-time employees as well as more part-time workers and volunteers.
Changes to Ethereum are made through Ethereum Improvement Proposals, which once accepted are implemented into a hard fork in the Ethereum blockchain.
Such a system is a huge risk to implement. Not all proposals receive consensus from the community. Some proposals have tried to reverse lost or hacked funds, but some argued that it conflicts with the Ethereum philosophy.
In one high profile proposal refund fork, called the DAO fork, the refund was rejected by a large part of the community, resulting in the Ethereum Classic fork.

Ethereum Classic uses the code as law. What happens is decided by the code and all actions occur voluntarily. That is, hacks cannot undone in Ethereum Classic.
NEO
NEO’s team is split into three groups, still led by cofounders Da Hongfei and Erik Zhang.
- The NEO Global Development Team (NGD) form the NEO organization, and are responsible for the success of the project.
- The City of Zion team are an independent community group who help develop, design and translate the NEO ecosystem. Funded by NGD, the team of over 20 volunteers have no counterparts at Ethereum.
- NEO Global Capital, an investment group in decentralized applications on the NEO platform.
It is the NEO council, part of the NGD team, who makes the strategic decision making. According to the white paper, it is “responsible to the NEO community with the promotion and development of the NEO ecosystem as its primary objectives”.
Unlike most other cryptocurrencies, NEO is quite centralized but is slowly decentralizing. The NEO team is in control of a large amount of NEO tokens to be used for development spending, stored in this wallet.
They also run a large, but decreasing proportion of the bookkeepers used in the NEO token’s consensus protocol, which gives them some control of the blockchain.
Funding
Ethereum
Ethereum has long been plagued by funding troubles, at one point only having one year’s worth of runway left before funding was dried up.

However, thanks to a range of private investors, Ethereum is now one of the most well funded blockchain projects with a runway over 4 years.
Their funds are spread across multiple currencies. In 2017, their assets were as follows:
- $15 million in fiat (mostly Euros and Swiss Francs)
- 500 Bitcoin
- 800,000 Ethereum
Ethereum is funded to about $700 million equivalent and enough resources to keep the project going for many years to come.
NEO
As explained in the inflation section, the NEO project has inflation funding from NEO tokens that have not yet been released into the ecosystem.
As a result, NEO is one of the few blockchain projects not seeking direct funding. Instead, the investments in NEO can be made directly by purchasing the coin and raising the value of NEO’s reserves. At current prices, their fund has a theoretical value of over 3 billion USD.
In 2017, NEO made a ground-breaking move when they announced that they would be paying back funding received its initial ICO, cithing “sufficient funds and resources to sustain the R&D and community development efforts in the years to come”.
The NEO project is fully funded, and have even begun directly funding community developers part of the City of Zion.
Token Divisibility
This is a minor point, but be advised that the NEO token is not divisible like Ethereum. On most exchanges, you will need to be careful to only withdraw whole numbers of NEO or the remaining fraction will be lost.
NEO and the Chinese Government
As the leader of blockchain projects in China, a large part of NEO’s fate is up to the Chinese regulators.
The Chinese Government have been disruptive in the past, blocking foreign crypto exchanges and banning new ICO’s. However, most industry analysts believe this will be a temporary ban as China takes the time to understand the space. It’s at least clear that China won’t be banning cryptocurrency permanently.
In fact, in its latest five-year plan, China outlined how blockchain technologies will be integrated into the economy.

China has put a stop to the blockchain free-for-all. Photo by Ming Chen.
Let’s also not forget that the Chinese public is highly receptive to digital payment methods. In many places, payments through WeChat and Alipay – two smartphone apps, are the norm.
For NEO and cofounder Da Hongfei, China’s commitment to give blockchain a chance seems clear. “We have pretty good communication with government (and) with the regulators. They don’t have a negative impression of NEO”, Hongfei explained at a NEO conference. “I think they like the technology and the way we deal with things. The government and (its) regulation won’t be an issue for us.”
Hongfei went on to justify the decisions of the Chinese Government, citing reckless crowdfunding and irresponsible investments, and assured that China just wanted more control over how it was implemented in Chinese markets.
Hongfei’s comments weren’t just speculation. Close NEO partner and blockchain application firm OnChain has worked with the Chinese government, and NEO has always maintained a strong emphasis on keeping in line with China’s industry regulations.
In the next section, I’ll explain exactly what NEO is doing to make the platform compliant, and how these efforts match up to Ethereum’s progress.
Diving Deep — The Technical Details
ICOs and Decentralized Applications (dApps)
If you’re familiar with the crypto space, then you might be aware that there are thousands of blockchain projects out there.
All of these projects do not need to run on the unique blockchains. Ethereum and NEO provide new projects, a blockchain to work with.
These decentralized applications can test their concepts, host their own initial coin offerings, then find their place in their respective markets without a development group working on the blockchain they use.
This is Ethereum’s focus. They want to empower entrepreneurs to create their own blockchain projects.
Smart Economy
The ideas explored below all roll into the idea of a smart economy.
NEO is the largest blockchain project with the goal of creating a smart economy, and their white paper outlines three key elements:
- Digital assets. Ownership of physical items can be managed digitally, and its value can split and shared between multiple people.
- Digital identities. Some transactions can occur anonymously. However in order to meet Government regulation, some users, particularly those who verify transactions and own assets, need to have an identity.
- Smart contracts. Agreements between people can be trustless if the parties agree on computer code that enforces the terms of the contract.
NEO’s ultimate goal is to build a smart economy, at least in China.
Smart Contracts
A large part of our economy is based on trust. As Da Hongfei puts it, entire industries are built on ensuring that things happen the way we expect: business law, financial accounting and Government regulations.

The solution, first proposed by researcher Nick Szabo (who could be ‘Satoshi Nakamoto’, the anonymous founder of Bitcoin) in 1996, is a smart contract.
The idea is that a transaction can occur without needing a credible third party, such as the Government, to guarantee and verify it. Instead, the guarantee of a smart contract comes from the fact that it is written in computer code that cannot be modified or lied to.
These properties come from the blockchain, and NEO and Ethereum already have smart contracts up and running.
Contracts can be made to only pay out if certain pre-programmed conditions are met. Some immediate possible applications of this are crowdfunded projects that only pay the developer if funding goals are reached, or mail deliveries that give back funds if the mail is not received.
Some smart contract proponents even believe that smart contracts could turn modern accounting, and with it every financial industry on its head.
Although the theory is not new, the technologies are. The vulnerabilities are unclear and if they do have a place in a modern economy, then Ethereum and NEO’s implementations are in their infancy stages.
Digital Assets
Who owns a house? In the modern world, your ownership of a property can only be proven by the Government., with a long, mutable database of names. In theory, there’s nothing stopping the Government from just deleting those records.
Although most are okay with trusting the Government, NEO and Ethereum want a trustless, decentralized system. The solution to proving you own your house is by creating a digital asset.

The NEO white paper puts it this way. “Digital assets are programmable assets that exist in the form of electronic data. With blockchain technology, the digitization of assets can be decentralized, trustful, traceable, highly transparent and free of intermediaries.” That is, a ledger of digital assets, linked to the people and entities that own them, can provide a record that proves that you own the house. It is always yours no matter what unless you use your secret private key to give it to somebody else.
Digital assets are only representations of assets, so their value can be split between multiple entities.
Both NEO and Ethereum support digital assets, but it is a key focus for NEO; they’re serious about digitizing the entire economy and are already preparing for industry use.
Protocol Differences
Blockchains need a consensus method in order to determine which transactions should be added and which are fraudulent.
Ethereum currently uses the same consensus protocol as Bitcoin, Proof of Work (PoW). In a PoW system, a group of miners try to solve difficult mathematical problems with computer hardware. If they find the solution, then they can decide which transactions to include next.
There are some major disadvantages to Proof of Work. Ethereum already uses a small country’s worth of electricity, it’s not infeasible to gather a majority amount of the hardware, then take control of entire blockchain, and it’s slow. This has led the Ethereum project down the road of switching to Proof of Stake (PoS).
In Proof of Stake, every token holder who puts up tokens has the chance to manage the next block. Putting up tokens is given a monetary incentive in the system. If the system detects fraudulent behaviour, it can automatically prevent it and seize the funds of the malicious user.
Proof of stake takes little to no electricity to run, and has the potential for much higher transaction bandwidths.

NEO uses the Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance (DBFT) protocol. In NEO’s DBFT system, token holders vote for bookkeepers to represent them. If 66% of the bookkeepers agree on the block, then it goes through.
Proposed by NEO cofounder Erik Zhang, DBFT provides a fast, highly secure mechanism for reaching a consensus, is protected against a range of possible attacks and helps to meet Government regulation.
However, it raises some issues about centralization. As mentioned in the currency governance section, the NEO team controls a large, but reducing number of the bookkeeping nodes, so it has substantial power over the network.
There are also some nuances to do with NEO’s second token, GAS. GAS is used for running smart contracts and for rewards for authenticating NEO transactions. One outcome of the system is that NEO transactions are completely free, and are paid for by the businesses using NEO’s network.
Although Ethereum is switching to Proof of Stake to improve speed and security, NEO has already made the switch and has decided on a specialised version of proof of stake they believe is best for a smart economy.
Transaction Speed
Payment processors such as VISA use a huge amount of computing power to manage and secure their networks. If NEO and Ethereum want to revolutionize entire industries, their systems must have theoretical maximums above the requirements to manage a smart economy.
The speed of a protocol is measured in transactions per second (tps).VISA’s network uses 2,000 tps. Further, the systems have current, practical speeds and theoretical maximum speeds that they may be able to reach in the future.
For NEO, its theoretical maximum is stated its white paper as 10,000 tps but has a current practical speed of around 1,000 tps.
In Ethereum’s case, it has a practical speed of 15 tps and theoretical speed of about 30 tps, but this will improve once Ethereum switches to Proof of Work.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is an issue that has plagued blockchains ever since their creation. A spike in Bitcoin transaction fees in late 2017 contributed to a crash in value, and Ethereum network fell apart when a kitten trading game became a little too popular.
Ethereum is addressing this with sharding technology in their Raiden upgrade, whilst NEO’s response is to collaborate with the Trinity project.

Both a full-fledged, serious attempts at solving the scalability problem.
NEO’s Regulatory Compliance — Digital Identities and Finality
It is in both NEO and the Chinese Government’s interests to bring the NEO project towards regulation.
There are two aspects of the NEO system that have been implemented in preparation for Chinese legislation:
Measure 1: Blockchain finality. If you’ve ever received Bitcoin before, you might be familiar with the idea of waiting for multiple blocks to pass before you can be ‘sure’ that the currency is yours. This occurs because disputes can occur under the proof of work system; just one user, if they manage to solve the block, can decide on what goes in it.
It’s then up to the next users to make a fork and reject the proposed transactions. Currencies such as Ethereum can have multiple valid forks running at once. It’s unlikely that this idea could ever work in a smart economy. Transactions need to be final and certain, or even the idea of ownership is blurred.
In NEO’s DBFT system, transactions are final once they are implemented into the blockchain. There’s no going back.
Measure 2: Digital identities. As mentioned in the digital asset section, NEO plans to integrate with the economy by allowing all financial assets to be represented and secured on their blockchain.
If this is to happen, then NEO needs to implement digital identities and signatures up to international standards, so they’ve built in the functionality to let it happen.
Ethereum’s Future — A Network With Privacy
One of Ethereum’s most ambitious projects is their partnership with privacy coin Zcash, and their plan to implement their privacy protocol, zkSNARKs.
‘Zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge’ (zKSNARKs) isn’t as complicated as it sounds. zkSNARKs is the privacy system behind Zcash, and its coming to Ethereum. It has two important characteristics:
- It offers an authentication method that allows two parties to verify they have the same information without revealing any of it to each other. Some good analogies are proving to someone you have more wealth without revealing any information about how much, or proving to a friend that you found Waldo in a game of Where’s Waldo without pointing to him. zkSNARKs is a system that can solve these problems and confirms privacy with mathematics.
- It takes a fair bit of resources. In zCash, using zkSNARKs to hide your transaction is optional. In fact, less than 10% of zCash is held with privacy protection. This is due to the higher transaction times and costs involved in executing the zkSNARKs protocol in a payment. As a result, most zCash in the network can actually be traced. Ethereum will also make privacy optional.

Zcash and Ethereum staff at a join meeting.
If you’re interested in learning more, read the Zcash blog posts or dive into Ethereum cofounder Vitalik Buterin’s in-depth explanations of the protocol.
Developer Offerings
Both NEO and Ethereum have something to offer to developers, and projects frequently switch between the two.

Advantages of developing on NEO:
- C#, Java, Python and Javascript, four of the most popular programming languages, are supported
- The transaction speed cap provides more room for growth
- New forks are impossible, providing the stability a project relying on another blockchain needs
- There are no transaction fees, which can reduce costs for dApps that need to frequently move funds around
- NEO actively optimises code before it is run
Advantages of developing on Ethereum:
- NEO’s philosophy of regulatory compliance gets in the way of some specific applications
- A huge existing community of developers (around 30 times more) who can provide support, guidance and manpower
- Ethereum’s dedicated programming language, Solidity, is designed solely for dApps
As both have unique advantages, it’s likely that they can coexist, even in such a competitive dApps space.
The Bottom Line
NEO and Ethereum both want to bring blockchain technologies to industry applications. They are still tweaking their networks, and neither are close to done, but Ethereum has already seen much more projects built on top of their code.
Ultimately, the debate boils down to whether NEO’s dominance in China, fast protocol and philosophy of regulatory compliance is enough to take down an already established Ethereum network dreaming equally big.
